Live Scripting
Overview
Live Scripting lets you build custom functions and macros directly inside your spreadsheet. Designed for both power users and developers, it combines ease of use with deep extensibility.
Key features of Live Scripting include:
- Custom functions: Define reusable macros and formula functions using standard syntax.
- Vectorized API: Perform data-science-style range operations with full spreadsheet context — presentation and interaction included.
- Interactive: Read/write from live spreadsheet data and events.
- Strongly Typed: Modern TypeScript with auto complete and real-time validation.
- Third-party libraries: Import 3rd party libraries.
Integrated Editor
The integrated editor, powered by Monaco Editor, provides an environment for writing, validating, and managing scripts. Core features include:
- Custom Functions: Create custom behaviors with
export-defined functions. - Auto Documentation:
ts-doccomments will generate tooltips and dropdown options. - Code Validation: Ensure reliability and catch errors with real-time syntax validation auto completion.
- Library Integration: The SheetXL API API Docs is ambiently available via the
SheetXLnamespace. 3rd party libraries are supported using unpkg, esm.sh, and in-memory bundling.
Access the editor through the Macro menu or by pressing Alt-F11.
Function Types
Live Scripting supports two types of exported functions: Formula Functions as Macro Functions.
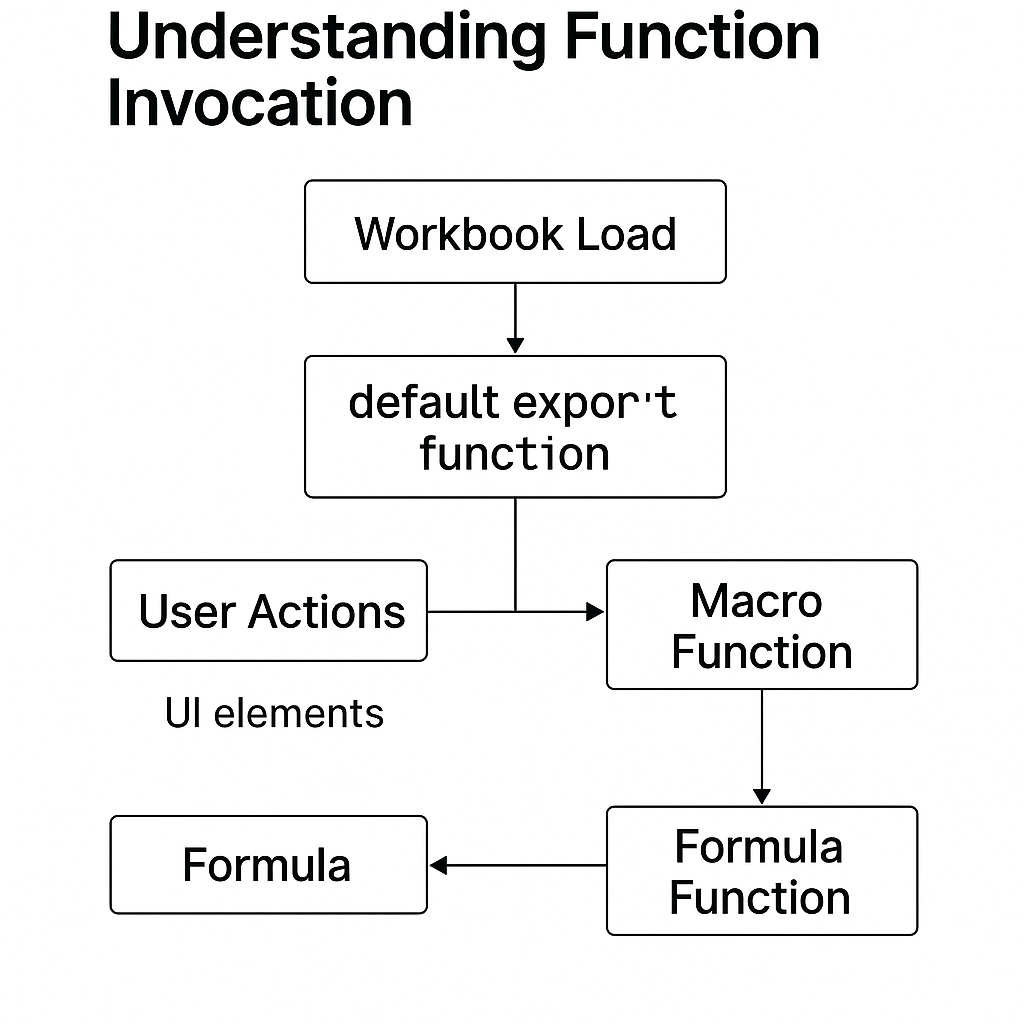
Figure 1: Scripting workflow overview
Formula Functions (User-Defined Functions - UDF)
While we use the term User-Defined Functions to align with the industry standard, All SheetXL built-in functions are defined using the same API and are made freely available at formulas source.
Purpose
Perform custom calculations or data transformations as part of the formula evaluation process.
Triggers
Activated during calculation or recalculation of cells that reference the function.
Inputs
Scalar,IRange,IRange[],IReferenceRange,IReferenceRange[],Scalar[], orScalar[][]- Variadic arguments using the ellipsis syntax (
...)
Return Values
- Must return a value that can be used in formulas or displayed in cells
voidis not permitted
User Interface
Available as dropdown options during formula editing.
Example
/**
* @summary Add 2 numbers.
*/
export function add(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b;
}
Macro Functions
Purpose
Automate tasks, respond to user interactions, and customize spreadsheet behavior.
Triggers
- Manual selection from the
Macrosmenu (with dialog input for parameters) - User interface elements like buttons or menus
- Workbook autorun scripts marked with the
default exportmodifier
Inputs
- Value objects such as:
ICell,ICellRange,ICellRanges,ISheet, andIWorkbook - Specific
ScalarorIRangeinputs (via user dialog prompt) - (Future support planned for MouseEvent and KeyboardEvent)
Return Values
- Must return
void,Promise<void>, or a cleanup function() => void - If provided, the cleanup function will be called when the macro is deregistered or the application shuts down gracefully
Clean up functions are not guaranteed to be called if the application shuts down unexpectedly.
User Interface
Available in the 'Macro' menu or associated with UI elements such as toolbars or menus.
Example
/**
* Prompts the user for a color.
*
* @summary Set Fill Color
*/
export function setFillColor(range: ICellRange, fillColor: IColor): void {
range.getStyle().setFill(fillColor);
}
Autorun
The Autorun macro is called once when a workbook is loaded.
/**
* Exporting a function as default will cause it to be run on workbook load.
*/
export default function main(workbook: SheetXL.IWorkbook): void {
// code that will only be executed once on load
}
The name of the default function is not important but main is used as convention.
Debugging
Debugging is supported using browser developer tools.
Insert a debugger; directive in your code to trigger breakpoints.
Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| IFunction | A unit of work, a function, that performs a specific task. Defined within a module and reusable. |
| IModule | A container for code, representing a conceptual file. Contains multiple scripts (functions) and metadata. |
| IScript | A interface/namespace for managing and interacting with scripting functionality (e.g., modules, utilities). |
Workbook
↳ getScripting(): IScript
↳ getModules(): IModuleCollection
↳ getByName("BudgetAnalysis"): IModule
↳ execute("calculateGrowthRate")
↳ execute("generateReport")
↳ getFunctionNames(): string[]
Comparison with VBA
For users familiar with VBA, SheetXL Live Scripting retains familiar concepts while introducing modern, safe, and embeddable development practices:
| Feature | VBA (Excel Desktop) | Office Scripts (Excel Web) | SheetXL (Live Scripting) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Languages | VBA (Visual Basic) | TypeScript (subset) | TypeScript (full) |
| Persistence State | Hidden workbook storage | ❌ Not supported | 'useState' serialization 🚧 |
| Script Format | Workbook-specific project | Workbook-linked JSON blob | JavaScript ESM |
| Initialization | Workbook_Open event | Task-based triggers | Default exported function |
| Macros | Sub routines | main() with limited access | Exported void functions |
| Formula Functions | UDFs via Function | ❌ Not supported | Exported value-returning functions |
| Global State | Module variables | ❌ No true globals | globalThis for shared state |
| Extensibility | COM / Add-ins (limited) | ❌ No imports | ES module imports |
| Security | Full system access | Microsoft-managed sandbox | Browser sandbox (iframe, CSP) |
